Once you’ve switched your ESP devices from the stock proprietary firmware to Tasmota, the good news is that future firmware upgrades to newer Tasmota versions should be straightforward. You just need to open your device’s web interface, and do an over-the-air (OTA) upgrade, or use something like TasmoAdmin to bulk-upgrade multiple devices. At least, that’s how it works in theory.
What you may find is that the update fails, due to a lack of storage space. So today, I’m going to outline four possible workarounds that you could try if your Tasmota firmware upgrades fail.
Why is there a lack of storage space?
Firstly, a bit about why this happens. You’re most likely to encounter this error with devices that use the ESP8266 chip. Some of these chips come with as little as one single megabyte of flash memory storage, and the standard build of Tasmota is 656 kilobytes (as of version 15.0.1 which is the latest at the time of writing). There simply isn’t enough space for both the current firmware and the new firmware to sit side-by-side ahead of the update process.
Now that we understand why the problem occurs, we can try some solutions.
Solution 1: gzipped binaries
As long as you’re upgrading from a version newer than Tasmota 8.2 (which came out over five years ago now), you can use the smaller gzipped binaries. This reduces the standard Tasmota 15.0.1 release binary down to 469 kilobytes.
However, on some of my devices, that was still too big – 656 plus 469 is more than 1024 kilobytes and exceeds the capacity of the 1 MB flash storage.
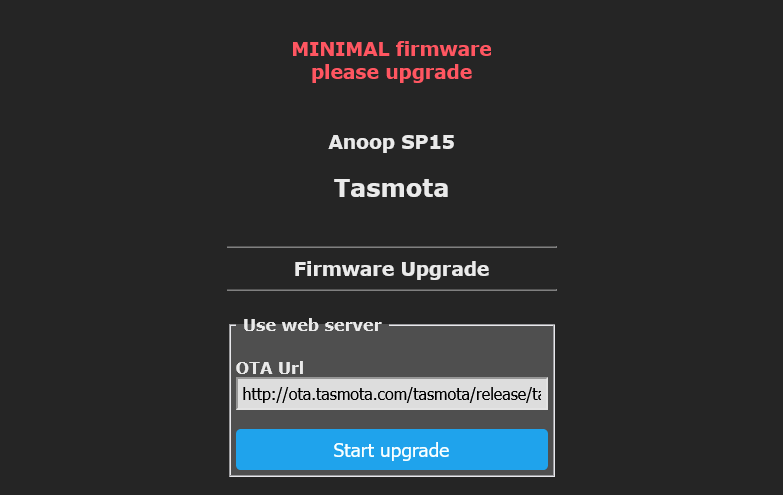
Solution 2: install tasmota-minimal first
There are a couple of slimmed down versions of Tasmota:
- tasmota-lite – a cut-down version of Tasmota without many of the sensors or drivers included
- tasmota-minimal – the bare-minimum of Tasmota which can’t do anything apart from be upgraded to the full firmware
What you can do is install the latest version of tasmota-minimal first, and then the latest standard version of Tasmota. tasmota-minimal is only 265 kilobytes, and so it’s small enough to fit alongside the standard firmware. Once installed, there’s then space for the full version to be installed.
When you do an OTA upgrade, this is the process that should happen – tasmota-minimal gets installed first, and then the full version. But if it doesn’t, you can do this manually yourself. Your device settings, such as the GPIO mappings and MQTT settings, will be retained during the process.
Solution 3: tethered firmware update
A tethered update is where you use another device, such as a PC, to update the firmware. This means physically connecting the device to the PC. It gets around the storage limitation as the firmware doesn’t need to be downloaded to the device running Tasmota first.
How easy this will be will depend on the device, and where it is. If you’re running Tasmota on a development board, such as a Wemos D1 or m5stack Atom, then you can plug in into your PC with a standard USB cable (as long as it’s a data and power cable). However, if your device is buried away somewhere inaccessible, or is a consumer device that requires disassembly and a USB to UART converter, then you may not want to do this every time a new version is released.
Solution 4: Compile Tasmota yourself
The standard builds of Tasmota cover most common use cases. However, as Tasmota is open source, you can compile it yourself. That way, you can create a smaller, customised build for your device that doesn’t include any extra functions that aren’t needed. There are tools available to do this, but this is really only for advanced users – especially as you’ll need to recompile the binaries for each release.
Solution 5: Switch to a different firmware
As I mentioned last month, Tasmota is not the only game in town. If you also use Home Assistant, then consider replacing Tasmota with ESPHome.
ESPHome has a higher learning curve, due to its use of YAML configuration files. But, once this is set up, it’s easier to compile new binaries each time a new version of ESPHome is released. And, if you’re lucky, you’ll be able to download a pre-built YAML file from the ESPHome Device Repository. Just be aware that it’s not as extensive as the Tasmota Supported Devices Repository – the ESPHome repository has details of around 600 devices compared to almost 3000 for Tasmota. I wasn’t able to find an exact match for ESPHome for my smart plugs, for example.
ESPHome has some other advantages. For example, you can edit the YAML configuration to tell Home Assistant what type of device is plugged in, say a light. That means it’ll appear in Home Assistant as a light, rather than a switch, without needing to use the Change device type of a switch helper.
As with solution four, having a smaller firmware binary will make future OTA updates easier, and these updates can be managed through Home Assistant.