It may surprise you to hear that we haven’t owned an air fryer until recently. They’re really popular, especially as, when compared with a regular convection oven, they can cook food faster and more cheaply. The cost of living crisis, and huge increase in energy bills, led many people towards buying these and I know lots of people who swear by them.
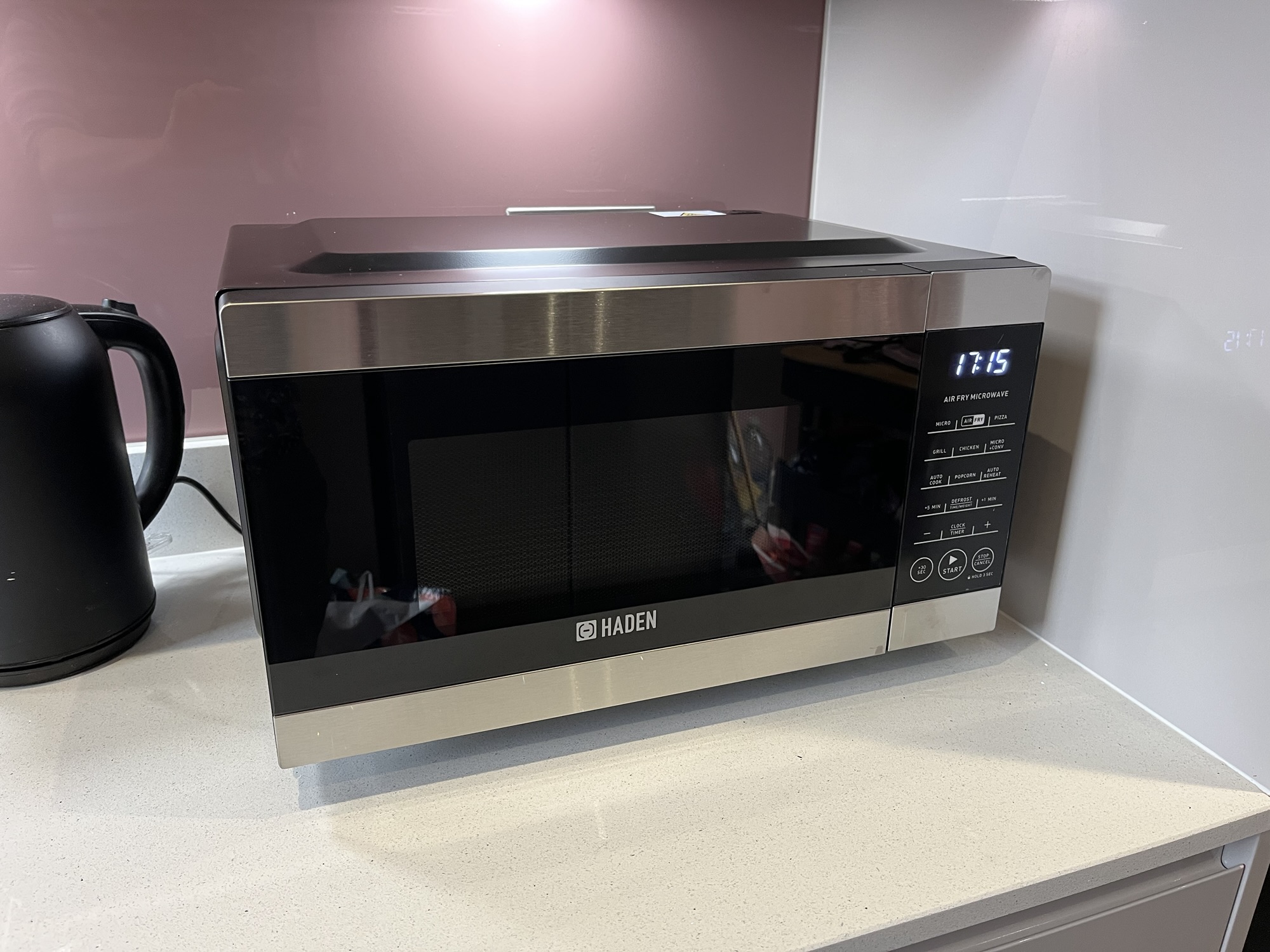
Anyway, we do now own an air fryer, in the form of this Haden 4-in-1 Air Fryer Microwave (sponsored link). It’s a microwave that can also act as an air fryer, a grill, and a convection oven. You can buy one from Amazon for £150, but we picked up ours from the middle aisle of our local Lidl for £120 a few weeks ago.
So why haven’t we owned an air fryer until now?
There are two key reasons why it’s taken us this long to buy an air fryer. The first is a lack of space; when we had our kitchen renovated in 2022, we ended up with less work surface space (but more usable space overall). There wasn’t really any room to keep a large air fryer out on the work surface, but nor did we want to be lifting a big air fryer out of a cupboard every time we wanted to use it. We also didn’t want to buy a small air fryer that wouldn’t serve our needs.
The second is that Christine wasn’t convinced by them. For her, Jay Rayner’s 2022 article criticising them was proof that they weren’t worth it. Also, in the kitchen renovation we had two full-size convection ovens installed, so there wasn’t much need.
This air fryer microwave gets around the space issue, by replacing one of the appliances that was already taking up space on our kitchen work surface. Our previous microwave pre-dates our relationship (which is 16 years as of tomorrow), and was only a cheap own-brand model from Tesco. It had a bit of metal missing, and as a 800 watt model, wasn’t as fast as newer microwaves on the market. Replacing it with an air fryer microwave would give us a more useful appliance, in the same space.
What it’s like to use
The controls are relatively straightforward – more so than our previous microwave. It defaults to microwave mode, but you can press the ‘grill’, ‘air fryer’ or ‘micro+conv’ buttons first to change the mode. In air fryer and oven mode, you select the temperature in degrees Celsius, and then the cooking time, before pressing the big start button. There are shortcut buttons to quickly add 30 seconds, a minute or five minutes. There are also presets for pizza, chicken and popcorn.
It is quite noisy, and the fan sometimes stays on after cooking – especially in air fryer mode.
As a microwave, it works well; the extra hundred watts of power reducing cooking time compared to our old microwave. Meanwhile, to use it as an air fryer, you pop a metal stand on top of the glass microwave plate with your food on. That means the food still rotates on the stand in air fryer mode, like it would in a regular microwave. In this mode, it can use up to 1500 watts of power, which is equivalent to dedicated stand-alone models.
We’ve yet to use the grill and convection oven modes, so I can’t comment on those.
Compromises
Any multi-function device is going to have some compromises, when compared with dedicated appliances. Taking our Instant Pot for example: it can slow cook, but you have to set the cooking temperature higher. This Haden air fryer microwave works well as a microwave, as mentioned above, but as an air fryer it isn’t as good as a dedicated appliance would be. The cooking times are longer; indeed, generally it needs to cook food for about the same time as in an oven. It does save a bit of time, as there’s no need to pre-heat it like you would with a regular oven, and it’s heating a smaller space and so should use less energy. But it’s not significantly faster than an oven in the way that a dedicated air fryer would be.
The other compromise is when you want to use multiple functions sequentially. For example, we air fried some sausages, and then wanted to use the microwave function to steam some broccoli to serve as part of the same meal. Unfortunately, the glass microwave plate was still really hot, and so not suitable for using with the plastic microwave steamer basket. As our old microwave wasn’t fit to pass on to a charity shop, we salvaged its glass plate before taking it to be recycled; thankfully this fits the new microwave and so we can swap the plates around if one gets too warm.
Verdict
So, should you consider a combination air fryer and microwave? If you’re pushed for space, then sure – you get what would normally be several separate appliances combined into one neat package. And at £150, it may be cheaper than buying the appliances individually, if you’re starting from scratch.
However, if you have the space for a microwave and an air fryer, and the money to spare, you’ll probably get better results from a dedicated air fryer than this combination model – especially if you plan to use it regularly. That being said, this Haden model is very much at the budget end, and others are available which may offer better results. There’s a Toshiba model (sponsored link) which includes a steamer basket and currently sells for £170 (normally £250). Panasonic’s microwaves tend to be highly rated, so you could consider their 4-in-1 model (sponsored link), but it’s currently £360. That’s three times as much as what we paid for our Haden model.