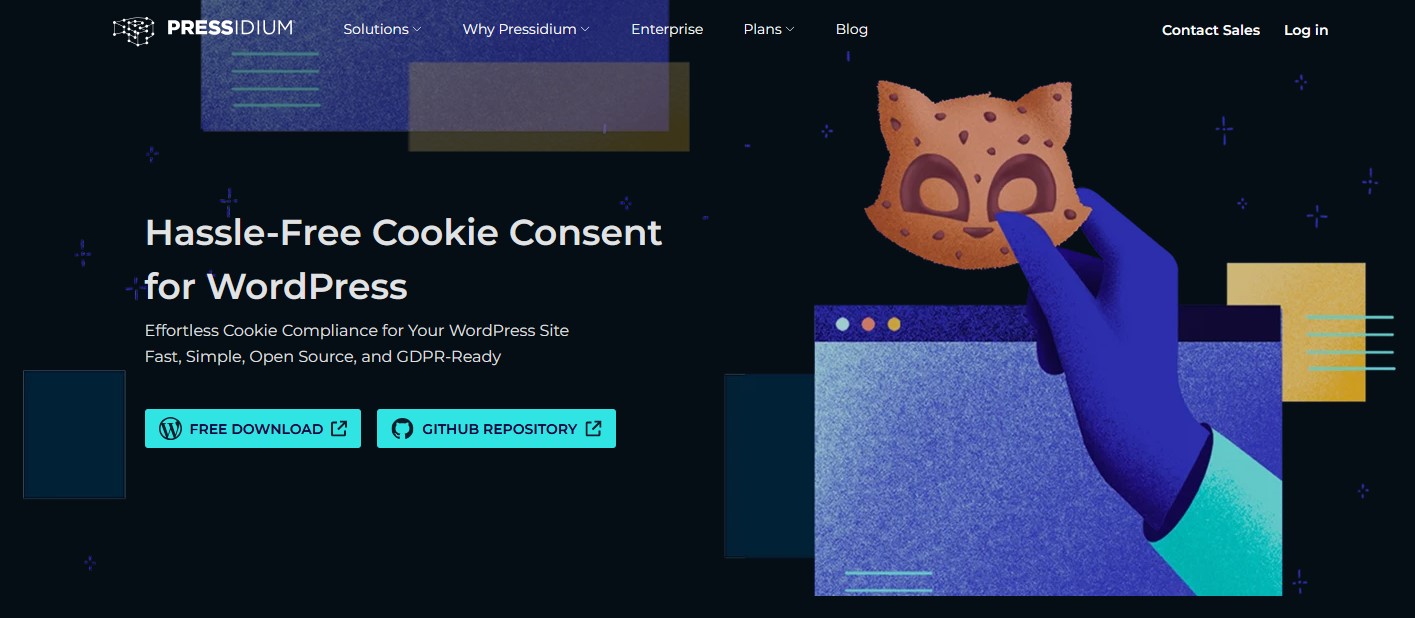
Someone anonymously emailed me recently to advise that my cookie consent banner was not compliant with current privacy regulations, and so I’ve swapped it for the Pressidium Cookie Consent WordPress plugin.
To date, I’ve been using the cookie consent banner component of the Toolbelt plugin (my review). As much as I like Toolbelt, it’s getting a bit old and it’s been almost five years since its cookie consent module was updated. As such, it basically says that ‘this site uses cookies, deal with it’, rather than giving users a choice to opt-out.
I’m a relatively privacy conscious person, to the extent that I tend to browse the web in Firefox with Enhanced Tracking Protection enabled alongside Privacy Badger. This extends to this web site – where possible, I avoid using third-party services. Indeed, the only cookies that you should experience are session cookies whilst browsing, that are deleted when you close your web browser, and Pressidium’s own cookie to remember your consent. For analytics, I use Koko Analytics (my review), which doesn’t need to set any third-party cookies.
Setting up Pressidium Cookie Consent
I deliberately went for this cookie consent plugin because it’s lightweight, and doesn’t need to use a third party web application. I’ve previously tried the CookieYes WordPress plugin, which is much more powerful and will auto-detect cookies to add to its consent forms. But it’s a big plugin designed for big sites that use lots of third-party tracking scripts. And as mentioned, I don’t.
Once installed, Pressidium Cookie Consent is relatively easy to set up and configure. You get a moderate amount of control over how the pop-up appears, and in turn the Cookie Settings box that users can view if needed. I like that it defaults to ‘accept all’ and ‘accept necessary’ – it annoys me when sites make you go through settings to reject all cookies and have you ‘object to legitimate interests’. In terms of its appearance, you can have it appear as a box or a strip, and control the colours.
In terms of specifying the cookies that users can consent to, this is where you’ll need to spend some time browsing your site in Private Browsing with Developer Tools open. Unlike the aforementioned CookieYes plugin, there isn’t a way of automatically detecting the cookies your site uses. Cookies can fit into four categories: necessary, analytics, targeting and preferences. Unfortunately, you can’t hide these categories, even if your site doesn’t use targeting cookies, for example.
If you use Google Tag Manager, then you can integrate this – I don’t. You can also include translations of the cookie consent popup and settings, and if you have API keys for OpenAI or Google Gemini, then it can use AI to generate these for you.
Free and open source
As it runs locally on your own WordPress instance, Pressidium Cookie Consent is free with no premium tier. The source code is on GitHub under the GPL 2.0 licence, and it’s in active development with a recent release for compatibility with the latest WordPress 6.9 release. Whilst it might not be as powerful as some WordPress cookie plugins, it should at least make your site compliant with GDPR and the like.