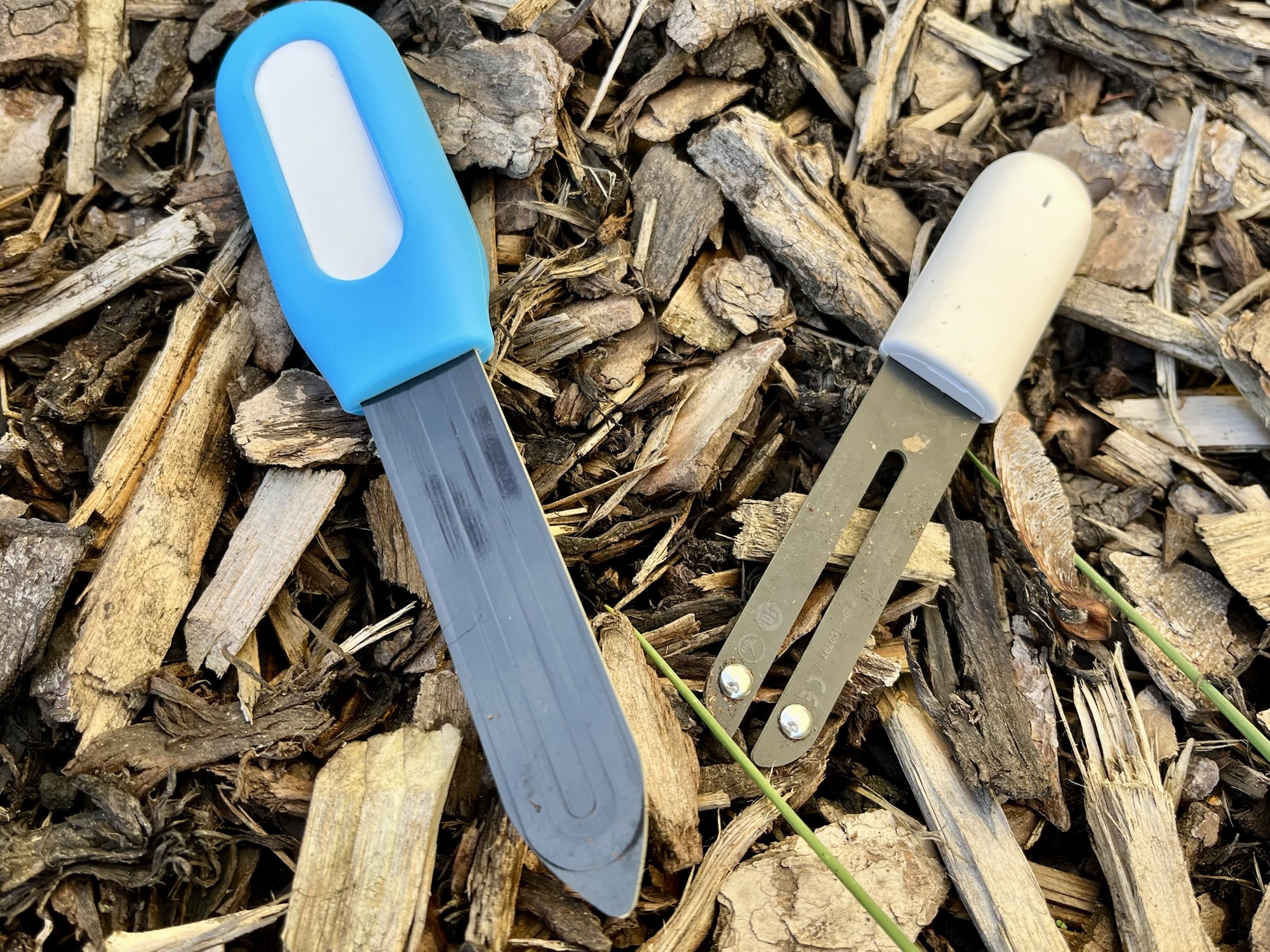
Search for ‘millennials house plants’ on Google and you’ll see lots of magazine articles about how people of our generation love our house plants. Alas, neither Christine or I are particularly good at keeping our house plants alive, apart from those in the already humid environment of our bathroom. So, I’ve been experimenting with electronic plant monitors to see if one will help us keep our plants thriving.
I’ve tried two different sorts of plant monitor: a Bluetooth Low Energy plant monitor from HHCC, and a Zigbee plant monitor from Haozee which works with the Tuya smart home platform. Both were bought from AliExpress.

HHCC Smart Flower Monitor
First to the HHCC model, which uses Bluetooth Low Energy. It’s sometimes known as ‘MiFlora’ and compatible devices are also sold under the Xiaomi brand. Of the two, it’s smaller, and offers more sensors; as well as detecting how much moisture is in the soil and the temperature, it’ll also try to measure how fertile the soil is, and the light intensity. It’s powered by a small CR2032 button battery which is replaceable. Officially, you should use the Flower Care app with it, but it also works with Home Assistant using the Xiaomi BLE integration.
The button battery should work for about six weeks before it needs replacing. Alas, these CR2032 batteries are not rechargeable, so you’ll need to take it to somewhere that recycles batteries and replace them when they run out of charge. At the time of writing, you can get 20 replacement CR2032 batteries for around £6, which should be enough to last you a couple of years.
Bluetooth Low Energy, as the name suggests, doesn’t have a long range. Therefore, if you are using this HHCC device with Home Assistant, you’ll need to have your device (or a Bluetooth proxy) in very close range.

Haozee Zigbee plant monitor
As you’ll see from the side by side photo at the top of this blog post, this Zigbee model is a bit bigger than the Bluetooth model. That’s because it takes two AAA batteries, rather than a CR2032 button battery. Consequently, battery life should be much longer – premium AAA batteries can typically hold up to 1100 mAh charge, compared to around 240 mAh in a CR2032 battery. Also, AAA batteries can be rechargeable.
The Zigbee signal should also be much stronger than Bluetooth Low Energy. I’ve certainly had fewer connection issues with this one compared to the HHCC model, even though the nearest Zigbee device is further away.
However, unlike the HHCC model, it doesn’t offer light or soil fertility sensors. You’ll just get the moisture level and temperature, as well as how much charge the battery has remaining. Also, if you’re planning to connect this to Home Assistant, be aware that it (probably) doesn’t support Home Assistant’s built-in ZHA integration. This was the reason why I set up Zigbee2MQTT.
The other disadvantage of Zigbee devices is the need for a hub or bridge of some sort. I use a Sonoff USB Zigbee dongle plugged into my Raspberry Pi running Home Assistant, but I imagine you’re supposed to use something like this Tuya Zigbee hub (sponsored link) and the Smart Life or Tuya phone apps. So whilst the Zigbee plant monitor itself was slightly cheaper than the Bluetooth model, there’s an initial setup cost if you don’t already have a Zigbee controller.
My recommendation
The HHCC Bluetooth plant monitor is fine if you just want to use the official Flower Care app, or have your plant very close to your Home Assistant device. The replacement batteries are cheap and you may not need any extra hardware to get it to work.
If you need a longer range, don’t want to replace batteries as often, and/or have other Zigbee devices already, get the Zigbee plant monitor. You can use standard rechargeable AAA batteries with it, and you’ll get a more reliable connection over long distances.