We’re back from our 2025 summer holiday in North Wales. Actually, we’ve been back a week now but it’s taken me a little time to sort the photos. I’ll be writing about the places we visited over the next couple of weeks, and today I’m starting with Conwy.
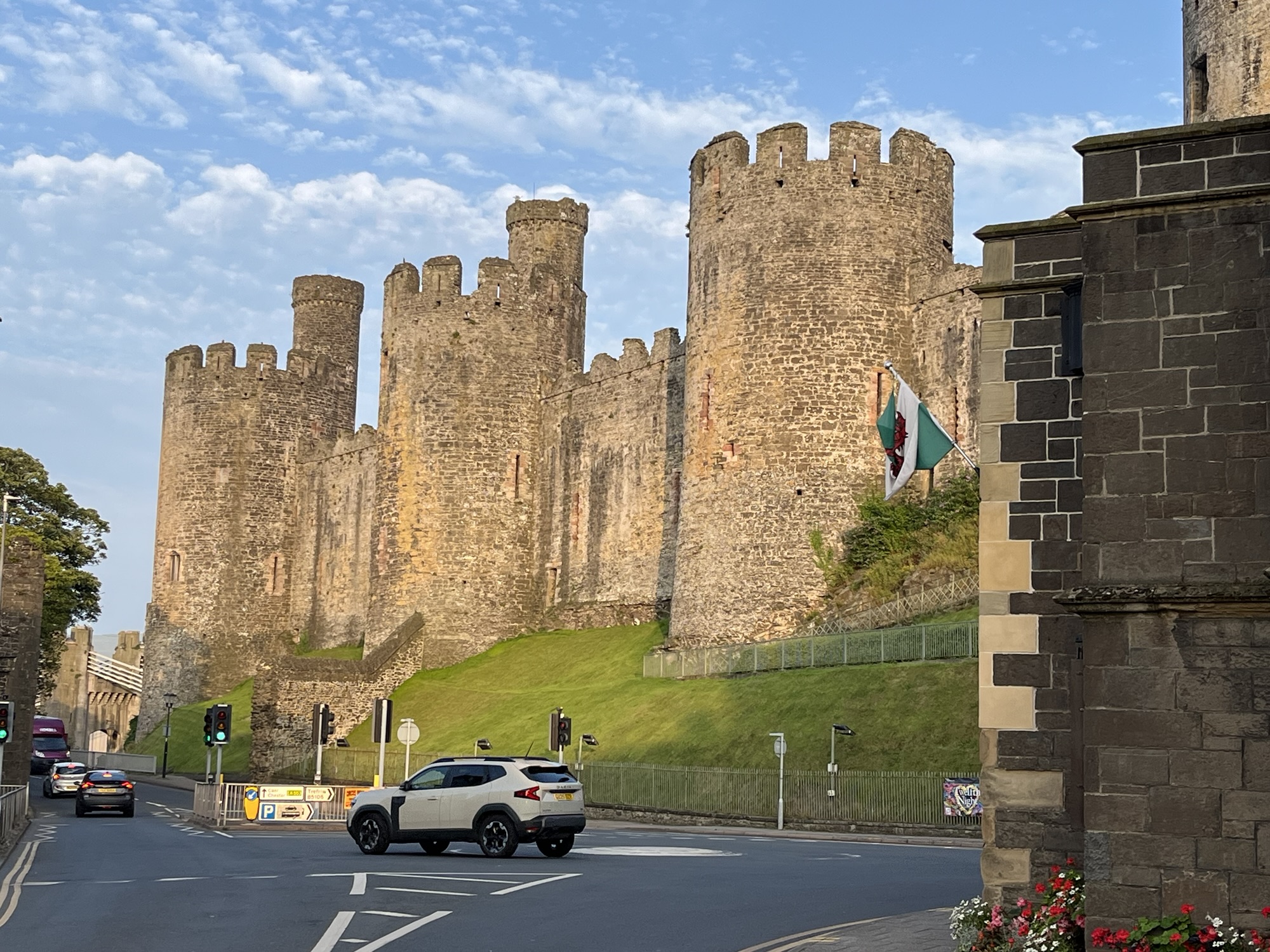
Situated on the North Wales coast, at the mouth of the Conwy Estuary, Conwy is a small town with a big castle. It retains its walls, which still run around almost all of the town and have only been breached in one location. Indeed, many stretches of wall are available to walk along.
Our rented cottage was just outside the walls, but was within walking distance.
A short history of Conwy
The town of Conwy was built by the English as a fortified town in the 13th Century. However, they weren’t the first people to occupy the site; in the 12th Century, some monks had founded an abbey there, known as Aberconwy Abbey. When the English, led by King Edward I, came along, they forced to monks to build a new abbey further up the Conwy Valley to the south. The castle was built first, followed by the town, and all use the same hard local stone. It’s probably due to the hardness of the stone, that the castle and walls have survived so long.
In the 14th Century, Welsh forces managed to seize the castle and the town, and held it for 3-4 months before negotiating a surrender. Inside the town, Aberconwy House was built around this time and remains the oldest surviving building within the town. It’s owned by the National Trust is open four days a week (Wednesday to Saturday) as a second-hand bookshop.
Whilst accessible by sea, it wasn’t until the 19th Century that road and rail access to Conwy became viable, and with it its rise as a tourist destination. In the late 20th Century, the whole town and castle became a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

Conwy bridges and tubes
The first bridge to be built across the Conwy Estuary was the Conwy Suspension Bridge, which will be 200 years old next year. It was designed by Thomas Telford, who was responsible for the first roads along the North Wales coast. The bridge still stands, albeit only open to foot traffic nowadays, and is managed by the National Trust. It’s open as a permissive footpath, so you don’t need to pay to cross it.
Telford’s suspension bridge is the world’s oldest surviving ‘modern’ suspension bridge. It could be seen as a dry run for another bridge that Telford designed, the Menai Bridge, further along the North Wales coast and spanning the Menai Strait between the British mainland and Anglesey.
Later on in the 19th Century, Robert Stephenson designed the Conwy Railway Bridge, which was built alongside Telford’s suspension bridge. This brought the North Wales Main Line railway to Conwy, on its way to Holyhead on Anglesey. This bridge is a tubular bridge – a pair of big metal girders, which were erected off site and lifted into place. Each hollow girder carries one of the two railway tracks. Stephenson also designed a tubular bridge to cross the Menai Strait, resulting in the Britannia Bridge. However, the Britannia Bridge was badly damaged in a fire in 1970, and was rebuilt to have two decks, with the railway below and the A55 North Wales Expressway up top.
By the 1950s, Telford’s suspension bridge was becoming a bottleneck, and so a third bridge was opened in 1958, the Pont Conwy (Conwy Bridge). I believe that it was at this point that a gap in Conwy’s walls was made to fit the wider road through. This is a much more plain, low-lying bridge that sits alongside Telford’s suspension bridge, to the north, with Stephenson’s tubular bridge to the south.
Whilst the Pont Conwy relieved one bottleneck, Conwy itself remained a pinch point for traffic heading to the port of Holyhead, where ferries go onwards to Ireland. The streets, and the gateways in the town’s walls are only wide enough for one lane of traffic, and to this day there’s a one-way system around the town. So, in the 1990s, the A55 North Wales Expressway was diverted into a tunnel, which runs under the Conwy Estuary. This was built using a (at the time) pioneering method of immersed tubes, buried in the riverbed. Nowadays, the A55 is all dual carriageway from Chester in England, through to Holyhead, apart from the Britannia Bridge. In fact, the road through Conwy and Colwyn Bay is a ‘secret motorway’, with motorway restrictions but standard green signs for a primary ‘A’ road.

Conwy Castle
The castle and town walls are managed by Cadw, the Welsh counterpart to English Heritage. Whilst the walls are free to walk on, you’ll need to pay to enter the castle. There’s a shop and visitor centre next to the town’s main car park, and this leads to a bridge across the B5106 Llanwrst Road and into the castle. Originally, there would have been a set of steps and a drawbridge, but a mini roundabout sits where the steps were.
Since it was constructed in the 13th Century, it’s fallen into ruin and then been repaired several times, but it was taken out of military use in the 17th Century following the English Civil War, and later stripped of all of its iron and lead. It’s now a ruin, although a reasonably well-preserved one, and visitors can climb most of the towers and walk along the walls. The last major investment in 2012 saw the construction of the new visitor centre, new information boards and several sculptures installed.
As it’s a ruin, there’s not masses to see there, although I feel that Cadw have done a better job of presenting the castle than their English counterparts did at Warkworth Castle. You could probably spend 1-2 hours here, depending on how interested you are and how many steps you’re willing to climb.
Other things to see in Conwy
On the waterfront, there’s the Smallest House in Great Britain, as recognised by Guinness World Records. Our nine-year-old went in on their own – we didn’t, as you have to pay. There are various boat tours on offer, mainly up and down the Conwy Estuary.
As you’d expect from a town that has a reputation for tourism, there are plenty of small shops to look around. Opposite the castle is The Knight Shop, which as well as selling various imitation swords and armour, has a fantastic range of mead. Including sparking mead, which I’ve never previously come across. We bought a bottle to try later.
Accessibility
Conwy has a railway station, although it’s a request stop with short platforms and not all trains that pass through are scheduled to stop. That being said, it’s a relatively easy walk from the nearby Llandudno Junction station, which has more regular services.
There’s a small car park inside the town walls, but there’s a larger one off Llanwrst Road which is linked to the town by a foot tunnel under the railway. I’m not aware of any public electric car chargers in or around the town, but there’s a Tesco and a Lidl at Llandudno Junction that we used for charging. There are regular bus services, and an open-top tourist bus regularly runs between Conwy and Llandudno.
For the castle, it’s possible to enter the castle without needing to climb any steps, but once inside you won’t be able to go into any of the towers without using stairs. Cadw and English Heritage members get into the castle for free, and there are discounts for Blue Light card holders, and members of the armed forces. Foster families with a Max Card can also get a discount, but people with disabilities will need to show proof of receipt of DLA or similar.