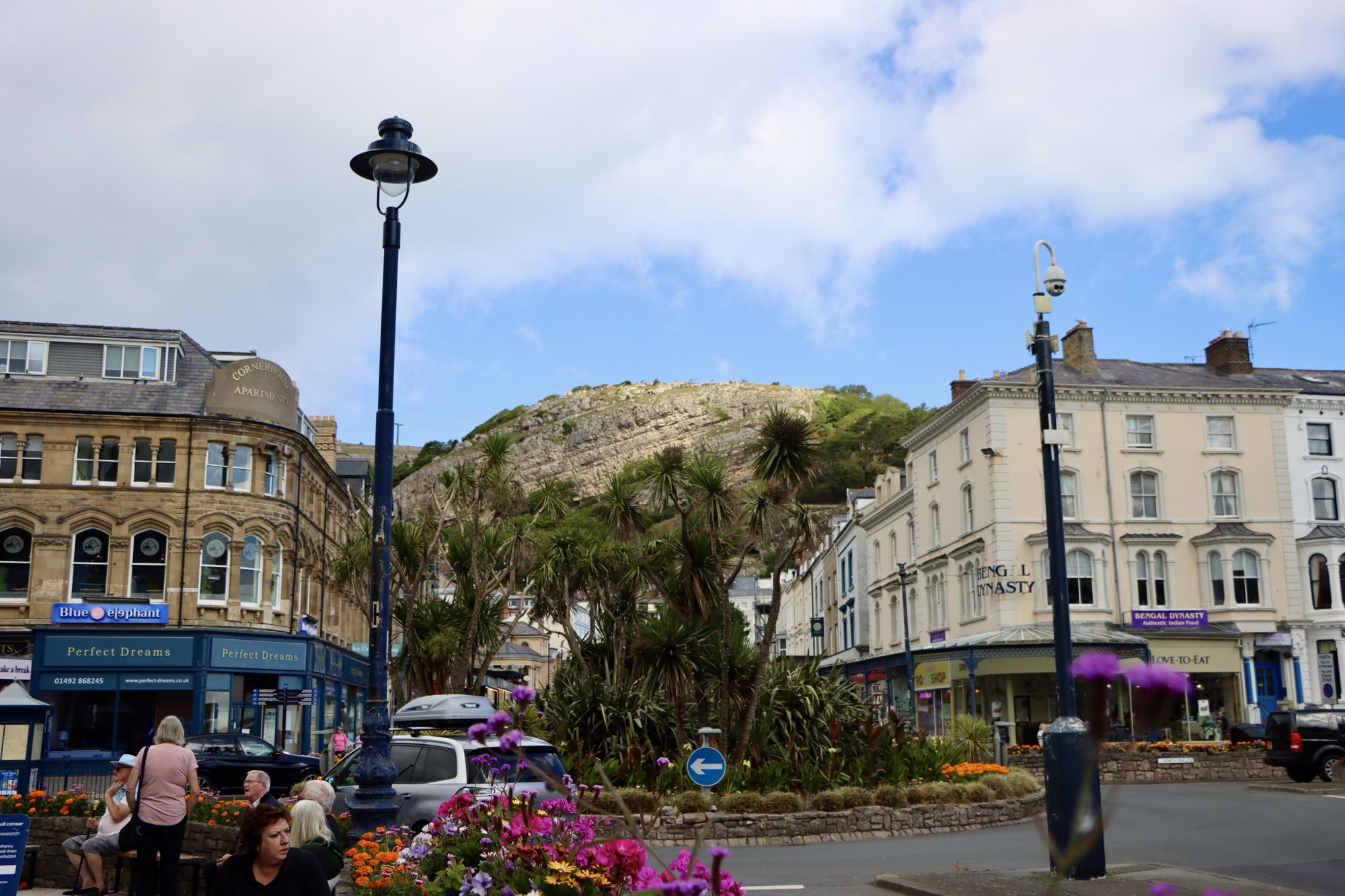
Directly north of Conwy, where we were staying, is Llandudno, a seaside resort that was largely developed in the mid 19th Century. Much of the land that Llandudno stands on was marshlands, owned by Lord Mostyn, and many of the buildings were planned and designed around the same time. As such, particularly along the seafront, there’s an aesthetically pleasing uniformity across the town.
Away from the seafront, the main street is Mostyn Street, and many shops have glass overhangs like those in Harrogate. However, it’s clear that the decline of the high street has affected Llandudno and I noticed a number of empty shops, including what looked like a large M&S. It turns out M&S merely moved to a new store a little further out of town, rather than leave the town entirely as it has done with Bradford, Hull and Huddersfield in recent years.

Llandudno Pier
Stretching out into the Irish Sea is the Grade II listed Llandudno Pier, dating from 1877. It’s the longest in Wales, and remains privately owned. It was also voted Pier of the Year this year, despite it recovering from damage from Storm Darragh at the end of last year. As piers go, there’s a decent mixture of shops – our nine-year-old particularly appreciated the Lego minifigures shop. At various times in its history, it’s been possible to catch ferry services from the far end of the pier, but no such services are currently running.

The Great Orme
The Great Orme is the name given to the headland to the north of Llandudno. As mentioned, Llandudno itself is former marshland and so is very flat, and mostly at sea level. Meanwhile, the Great Orme rises to a height of just over 200 metres and is a prominent feature on the landscape. Because it’s surrounded by low-lying land, the Great Orme feels like a mountain, but it isn’t – parts of the village of Queensbury, near Bradford, are twice as high for example. It would need to be around three times taller – 610 metres – to be considered a proper mountain.
Much of the Great Orme is owned by the National Trust, but it’s managed on a day-to-day basis by the local authority who operate the facilities there. In the Summit Complex, there’s a café and a shop; there also appeared to be a bar, but this was closed when we visited. There’s also a visitor centre with history about the Great Orme, including its lighthouse.
Across the Great Orme are plenty of sheep, and some Kashmir goats which are descended from a pair gifted to Queen Victoria. There’s also a species of shrub called the Wild Cotoneaster, which is critically endangered and only found on the Great Orme.
The Great Orme Mines
Inside the Great Orme are seams of malachite, a copper ore, mixed amongst the sandstone. These have been mined for over 4000 years, although mining activity ended in the late 19th Century. In 1987, ahead of the building of a new car park, an archaeological dig was ordered, and the mines were rediscovered. That car park never got built, as the dig is still ongoing, with part of it opened as the Great Orme Bronze Age Copper Mines.
The opening up of the mines changed our understanding of Bronze Age history; it was previously thought that bronze tools weren’t used in Britain until the arrival of the Romans. But tools were found in the mines, made using copper from the mine and tin imported from Cornwall.
Today, you can go into the first two levels of the mines, which go around 18 metres underground. This includes a huge cavern, which was excavated by hand and is now home to several stalagmites and stalactites. So far, nine levels have been excavated, with more likely to be found as the excavation continues. Our nine-year-old enjoyed it, and it was good to compare it with the 19th and 20th Century mines that we visited last year at Beamish and the National Coal Mining Museum for England.

The Great Orme tramway
There are a few ways up the Great Orme. If you’re feeling especially athletic, you can walk up, but it’s quite a steep climb. You can drive – there’s a car park at the summit – or catch a bus. Both standard public buses, and an open top minibus for tourists, run to the summit.
You can also travel by cable car, from just above the pier in Llandudno. But, for me, the best way up is on the Great Orme Tramway. Opened in 1902, this runs from Llandudno up to the summit, and is Britain’s last surviving cable-powered tramway. It’s actually two separate tramways; passengers have to alight at the halfway station to switch from one tram to the other. The halfway station, rebuilt in 2001, also doubles as the workshops, and there are large windows so that you can see the winding gear for the cables.
The tramcars are all original, although the 2001 upgrade did introduce some modern equipment. Whilst the tramcars were hauled using cables, they also previously used overhead cables for communication. The 2001 upgrade replaced this with a radio system, so whilst the tramcars retain short trolley poles at each end, they’re no longer used in service.
The lower section of the line runs along several streets, which is unusual for a cable-powered tramway. Both sections operate on the funicular principal, so as one tramcar goes up, another goes down. It’s mostly single track, with each section having a passing place in the middle.
Accessibility
Llandudno station is at the end of a short branch line from Llandudno Junction, and receives regular local services from Chester and Manchester. Less frequent services run to Cardiff; in the past, direct trains to London Euston have operated but not since 2008.
We parked at the Victoria Shopping Centre, which is central to the town and has a multi-storey car park. We didn’t need to charge our electric car there, but there are 12 Type 2 chargers offering up to 22 kW available, on the Roam network. As mentioned, there is also a car park at the top of the Great Orme.
The pier is all on one level. The Great Orme tramway has limited capacity for wheelchairs, which need to be folded whilst on board, and there are steps up to the tramcars.