Home Assistant includes support for go2rtc, a streaming video application, which can be used to monitor and store footage from CCTV cameras. Since the November 2024 (2024.11) release of Home Assistant, go2rtc has been included in Home Assistant’s Default Config, which means that integration is loaded automatically on startup. If you don’t have any cameras to monitor in Home Assistant, this can mean some warnings appearing in your logs, and potentially slow Home Assistant down.
There are two ways to disable go2rtc if you don’t need it – a hard way and an easy way.
Hard way: Disable Home Assistant’s Default Config
You can tell Home Assistant not to load the Default Config. This gives you more control over which built-in integrations are loaded when you boot Home Assistant up, however, it means editing your configuration.yaml file. You’ll need to delete the ‘default_config:‘ line, and then create new entries for all the parts of the default configuration that you want to keep. This may be fine for simple installations, but for most users, this will add more complexity. I wouldn’t recommend this personally.
Easy way: Using HACS integrations
There are two HACS integrations that you need to install:
These are not in the standard HACS repository, so you’ll need to open HACS, click on the three dots in the top right, select ‘Custom Repositories’ and then add the Github URLs in turn. You’ll need to install Early Loader first, restart Home Assistant, and then install Default Config Exclude next.
Once installed, you’ll still need to edit your configuration.yaml file, but instead you’ll only have to add a small block. Here’s mine:
default_config_exclude:
- go2rtc
- stream
- cloud
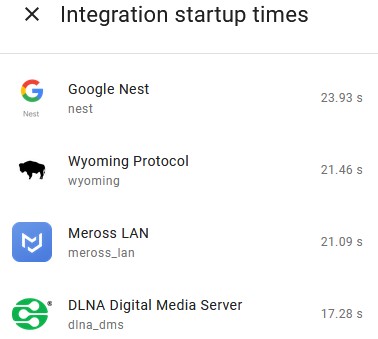
- myWhat you’ll notice is that I’ve added some other integrations – stream, Home Assistant Cloud, and My Home Assistant. If you don’t have any cameras, then not only do you not need go2rtc, you probably don’t also need stream either. I don’t use Home Assistant Cloud or My Home Assistant, so I’ve disabled these too. As well as starting up a little quicker, Home Assistant also now uses slightly less RAM than before.